Подключение и настройка SKR 1.4 +TMC2209 +датчик филамента
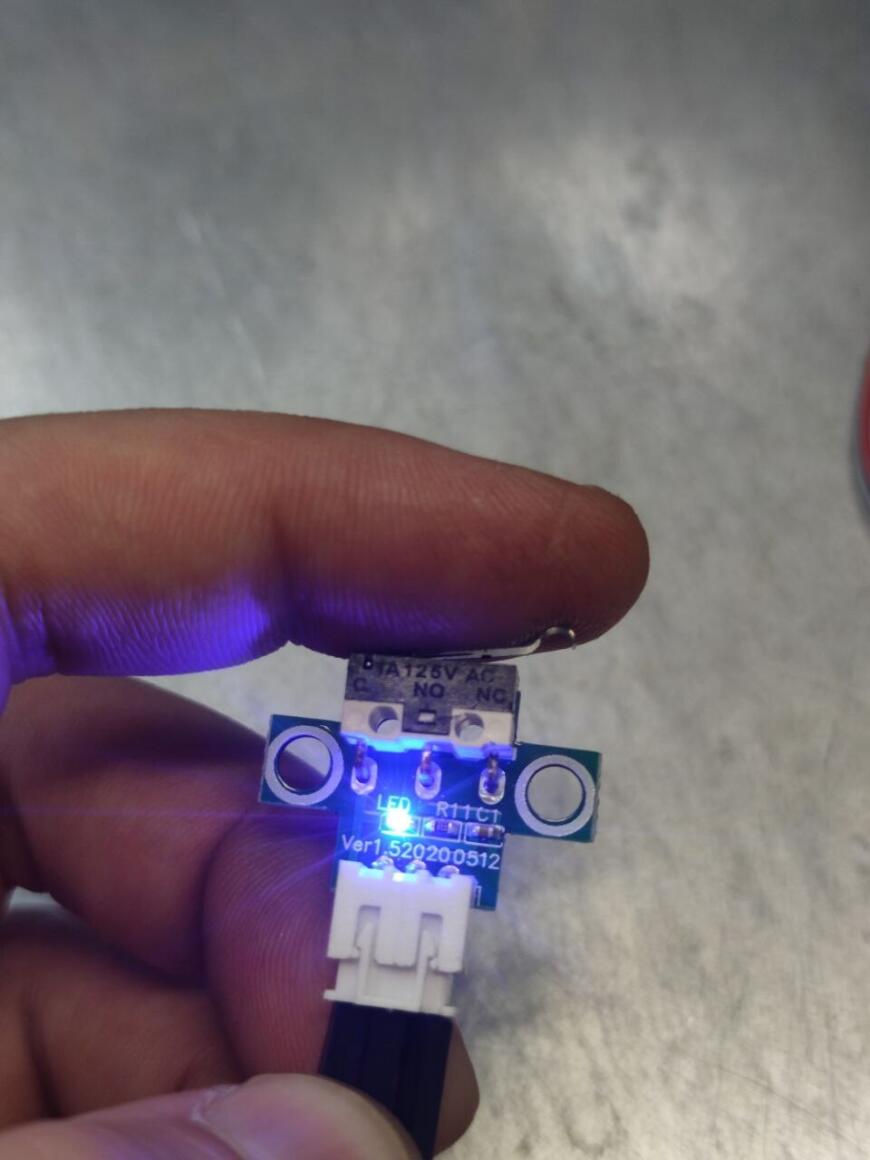
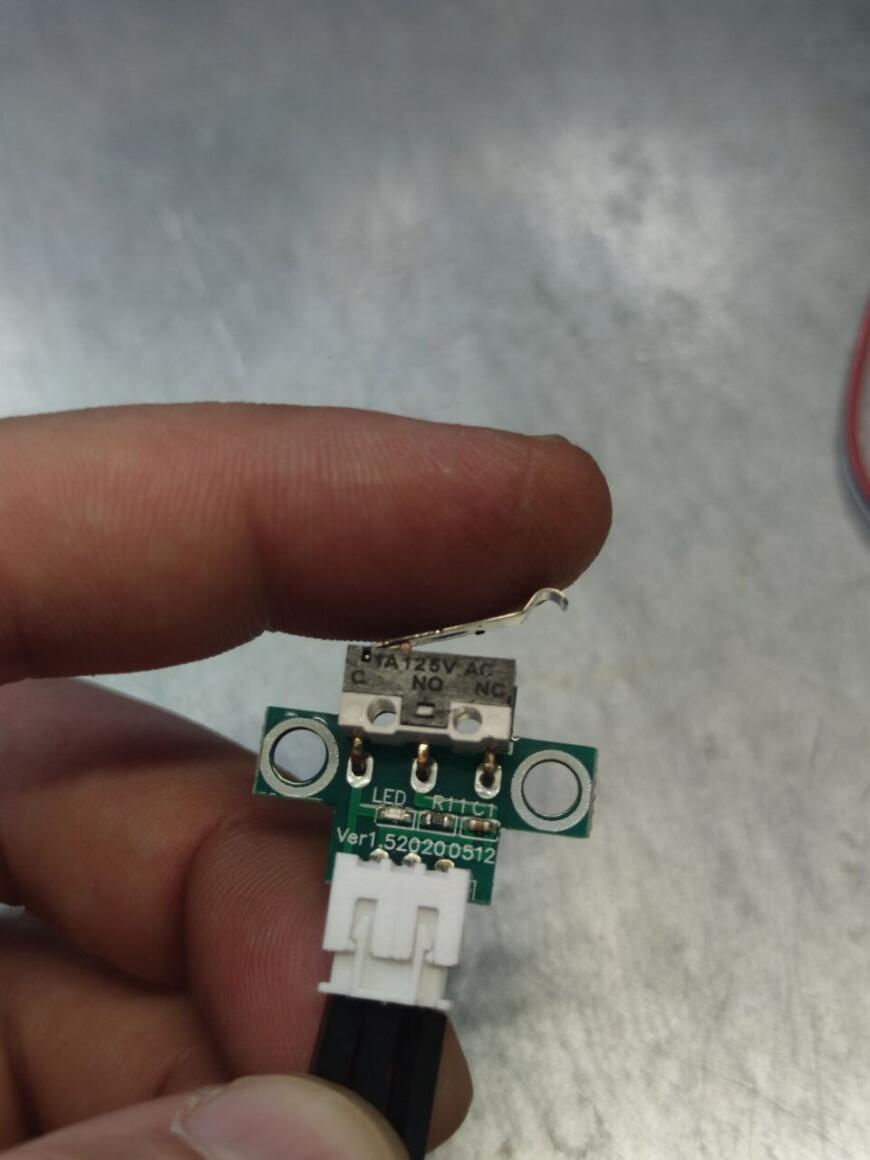
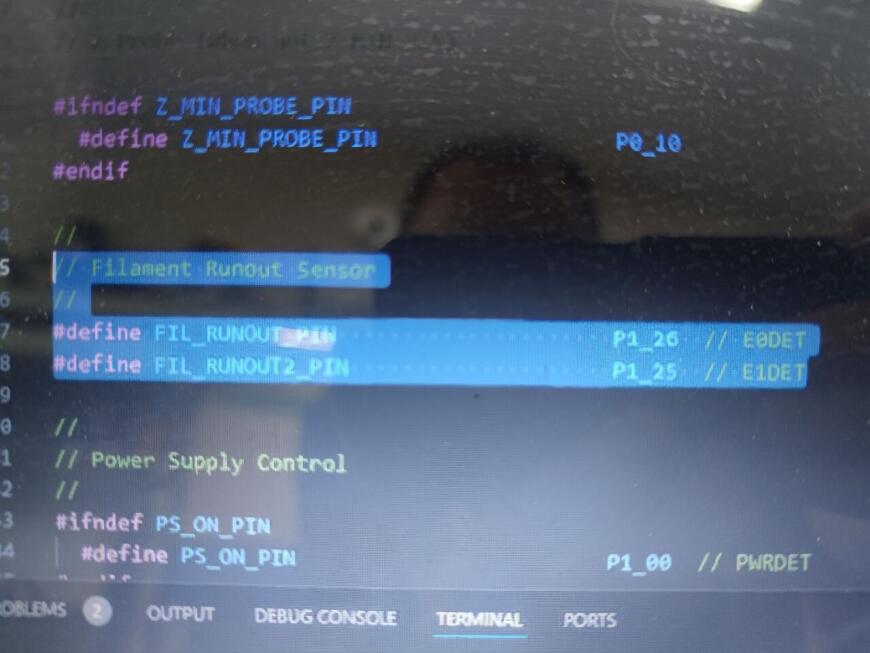
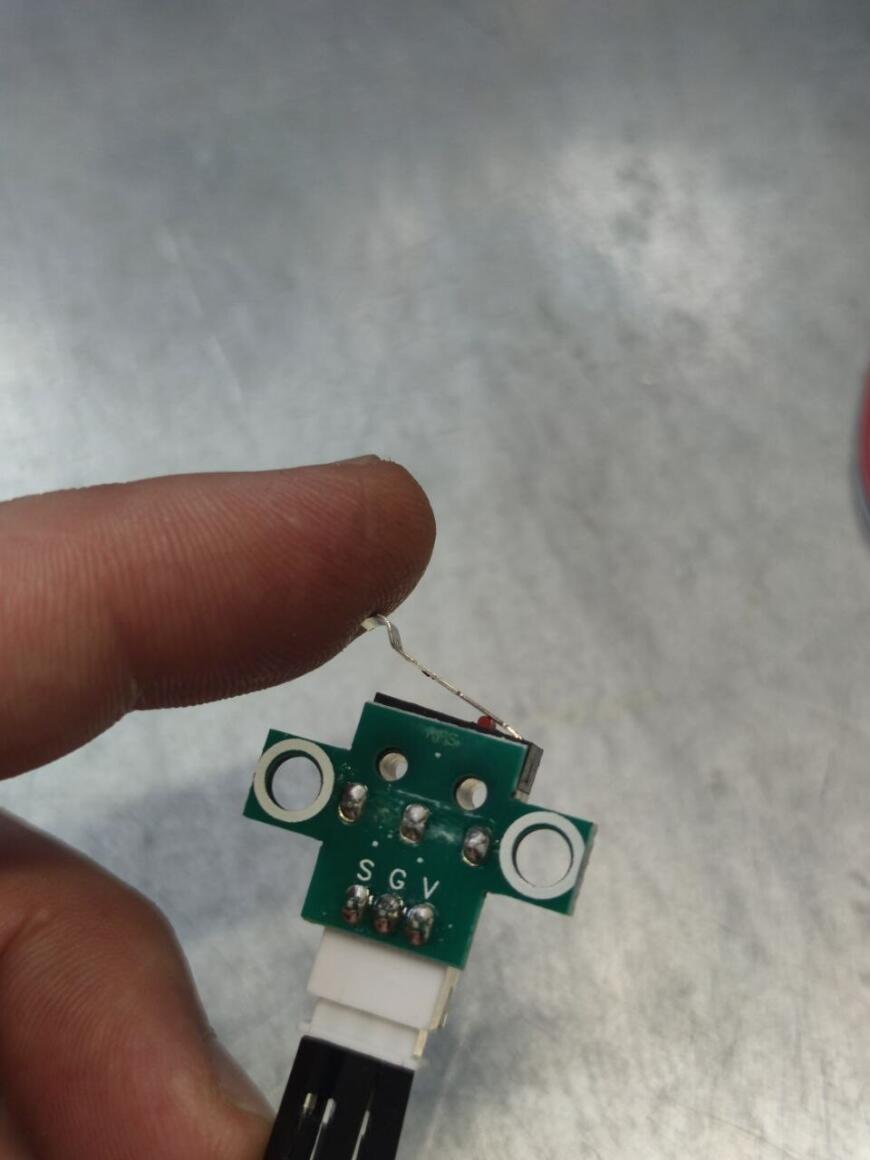
Всех приветствую Подключаю датчик окончания филамента в SKR 1.4 +TMC2209, принтер ender 3. Делал все по инструкции схожей темы на форуме: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=TrDJmYcZ0Ic&t=74s, все что на этом видео повторил за исключением выбора дисплея- у меня дисплей CR-10- обычный от ender 3. Прошивка компилируется. Запускаю печать, делаю имитацию обрыва нити, принтер останавливается на паузу, просит заменить пруток. После замены прутка, снова уходит в паузу- не срабатывает концевик. Концевик филамента проверил в программе репитер хост, все работает: в разомкнутом состоянии "filament: open" , вставляю пруток, светодиод загорается о срабатывании "filament: triggered". Подключение концевика правильное- проверял с обратной стороны на плате BTT SKR 1.4. Дополнительно в прошивке посмотрел какой пин задействован на эту функцию- pin_26 // E0DET. Помогите разобраться почему не срабатывает датчик? Модель датчика на фото.
#ifndef MOTHERBOARD
#define MOTHERBOARD BOARD_BTT_SKR_V1_4
#endif
/
* Select the serial port on the board to use for communication with the host.
* This allows the connection of wireless adapters (for instance) to non-default port pins.
* Serial port -1 is the USB emulated serial port, if available.
* Note: The first serial port (-1 or 0) will always be used by the Arduino bootloader.
*
* :[-1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]
*/
#define SERIAL_PORT -1
/
* Serial Port Baud Rate
* This is the default communication speed for all serial ports.
* Set the baud rate defaults for additional serial ports below.
*
* 250000 works in most cases, but you might try a lower speed if
* you commonly experience drop-outs during host printing.
* You may try up to 1000000 to speed up SD file transfer.
*
* :[2400, 9600, 19200, 38400, 57600, 115200, 250000, 500000, 1000000]
*/
#define BAUDRATE 115200
//===========================================================================
//============================= Mechanical Settings =========================
//===========================================================================
// @section machine
// Enable one of the options below for CoreXY, CoreXZ, or CoreYZ kinematics,
// either in the usual order or reversed
//#define COREXY
//#define COREXZ
//#define COREYZ
//#define COREYX
//#define COREZX
//#define COREZY
//#define MARKFORGED_XY // MarkForged. See https://reprap.org/forum/read.php?152,504042
//#define MARKFORGED_YX
// Enable for a belt style printer with endless "Z" motion
//#define BELTPRINTER
// Enable for Polargraph Kinematics
//#define POLARGRAPH
#if ENABLED(POLARGRAPH)
#define POLARGRAPH_MAX_BELT_LEN 1035.0
#define POLAR_SEGMENTS_PER_SECOND 5
#endif
//===========================================================================
//============================== Endstop Settings ===========================
//===========================================================================
// @section endstops
// Specify here all the endstop connectors that are connected to any endstop or probe.
// Almost all printers will be using one per axis. Probes will use one or more of the
// extra connectors. Leave undefined any used for non-endstop and non-probe purposes.
#define USE_XMIN_PLUG
#define USE_YMIN_PLUG
#define USE_ZMIN_PLUG
//#define USE_IMIN_PLUG
//#define USE_JMIN_PLUG
//#define USE_KMIN_PLUG
//#define USE_UMIN_PLUG
//#define USE_VMIN_PLUG
//#define USE_WMIN_PLUG
//#define USE_XMAX_PLUG
//#define USE_YMAX_PLUG
//#define USE_ZMAX_PLUG
//#define USE_IMAX_PLUG
//#define USE_JMAX_PLUG
//#define USE_KMAX_PLUG
//#define USE_UMAX_PLUG
//#define USE_VMAX_PLUG
//#d
Артем, [16.09.2024 16:37]
efine USE_WMAX_PLUG
// Enable pullup for all endstops to prevent a floating state
#define ENDSTOPPULLUPS
#if DISABLED(ENDSTOPPULLUPS)
// Disable ENDSTOPPULLUPS to set pullups individually
//#define ENDSTOPPULLUP_XMIN
//#define ENDSTOPPULLUP_YMIN
//#define ENDSTOPPULLUP_ZMIN
//#define ENDSTOPPULLUP_IMIN
//#define ENDSTOPPULLUP_JMIN
//#define ENDSTOPPULLUP_KMIN
//#define ENDSTOPPULLUP_UMIN
//#define ENDSTOPPULLUP_VMIN
//#define ENDSTOPPULLUP_WMIN
//#define ENDSTOPPULLUP_XMAX
//#define ENDSTOPPULLUP_YMAX
//#define ENDSTOPPULLUP_ZMAX
//#define ENDSTOPPULLUP_IMAX
//#define ENDSTOPPULLUP_JMAX
//#define ENDSTOPPULLUP_KMAX
//#define ENDSTOPPULLUP_UMAX
//#define ENDSTOPPULLUP_VMAX
//#define ENDSTOPPULLUP_WMAX
//#define ENDSTOPPULLUP_ZMIN_PROBE
#endif
// Enable pulldown for all endstops to prevent a floating state
//#define ENDSTOPPULLDOWNS
#if DISABLED(ENDSTOPPULLDOWNS)
// Disable ENDSTOPPULLDOWNS to set pulldowns individually
//#define ENDSTOPPULLDOWN_XMIN
//#define ENDSTOPPULLDOWN_YMIN
//#define ENDSTOPPULLDOWN_ZMIN
//#define ENDSTOPPULLDOWN_IMIN
//#define ENDSTOPPULLDOWN_JMIN
//#define ENDSTOPPULLDOWN_KMIN
//#define ENDSTOPPULLDOWN_UMIN
//#define ENDSTOPPULLDOWN_VMIN
//#define ENDSTOPPULLDOWN_WMIN
//#define ENDSTOPPULLDOWN_XMAX
//#define ENDSTOPPULLDOWN_YMAX
//#define ENDSTOPPULLDOWN_ZMAX
//#define ENDSTOPPULLDOWN_IMAX
//#define ENDSTOPPULLDOWN_JMAX
//#define ENDSTOPPULLDOWN_KMAX
//#define ENDSTOPPULLDOWN_UMAX
//#define ENDSTOPPULLDOWN_VMAX
//#define ENDSTOPPULLDOWN_WMAX
//#define ENDSTOPPULLDOWN_ZMIN_PROBE
#endif
// Mechanical endstop with COM to ground and NC to Signal uses "false" here (most common setup).
#define X_MIN_ENDSTOP_INVERTING false // Set to true to invert the logic of the endstop.
#define Y_MIN_ENDSTOP_INVERTING false // Set to true to invert the logic of the endstop.
#define Z_MIN_ENDSTOP_INVERTING false // Set to true to invert the logic of the endstop.
#define I_MIN_ENDSTOP_INVERTING false // Set to true to invert the logic of the endstop.
#define J_MIN_ENDSTOP_INVERTING false // Set to true to invert the logic of the endstop.
#define K_MIN_ENDSTOP_INVERTING false // Set to true to invert the logic of the endstop.
#define U_MIN_ENDSTOP_INVERTING false // Set to true to invert the logic of the endstop.
#define V_MIN_ENDSTOP_INVERTING false // Set to true to invert the logic of the endstop.
#define W_MIN_ENDSTOP_INVERTING false // Set to true to invert the logic of the endstop.
#define X_MAX_ENDSTOP_INVERTING false // Set to true to invert the logic of the endstop.
#define Y_MAX_ENDSTOP_INVERTING false // Set to true to invert the logic of the endstop.
#define Z_MAX_ENDSTOP_INVERTING false // Set to true to invert the logic of the endstop.
#define I_MAX_ENDSTOP_INVERTING false // Set to true to invert the logic of the endstop.
#define J_MAX_ENDSTOP_INVERTING false // Set to true to invert the logic of the endstop.
#define K_MAX_ENDSTOP_INVERTING false // Set to true to invert the logic of the endstop.
#define U_MAX_ENDSTOP_INVERTING false // Set to true to invert the logic of the endstop.
#define V_MAX_ENDSTOP_INVERTING false // Set to true to invert the logic of the endstop.
#define W_MAX_ENDSTOP_INVERTING false // Set to true to invert the logic of the endstop.
#define Z_MIN_PROBE_ENDSTOP_INVERTING false // Set to true to invert the logic of the probe.
// Enable this feature if all enabled endstop pins are interrupt-capable.
// This will remove the need to poll the interrupt pins, saving many CPU cycles.
//#define ENDSTOP_INTERRUPTS_FEATURE
/
* Endstop Noise Threshold
*
* Enable if your probe or endstops falsely trigger due to noise.
*
* - Higher values may affect repeatability or accuracy of some bed probes.
* - To fix noise install a 100nF ceramic capacitor in parallel with the switch.
* - This feature is not required for common micro-switches mounted on PCBs
* based on the Makerbot design, which already have the 100nF capacitor.
*
* :[2,3,4,5,6,7]
*/
//#define ENDSTOP_NOISE_THRESHOLD 2
Артем, [16.09.2024 16:37]
// Check for stuck or disconnected endstops during homing moves.
//#define DETECT_BROKEN_ENDSTOP
//=============================================================================
//============================== Movement Settings ============================
//=============================================================================
// @section motion
/
* Default Settings
*
* These settings can be reset by M502
*
* Note that if EEPROM is enabled, saved values will override these.
*/
/
* With this option each E stepper can have its own factors for the
* following movement settings. If fewer factors are given than the
* total number of extruders, the last value applies to the rest.
*/
//#define DISTINCT_E_FACTORS
/
* Default Axis Steps Per Unit (linear=steps/mm, rotational=steps/°)
* Override with M92
* X, Y, Z [, I [, J [, K...]]], E0 [, E1[, E2...]]
*/
#define DEFAULT_AXIS_STEPS_PER_UNIT { 160, 160, 800, 820 }
/
* Default Max Feed Rate (linear=mm/s, rotational=°/s)
* Override with M203
* X, Y, Z [, I [, J [, K...]]], E0 [, E1[, E2...]]
*/
#define DEFAULT_MAX_FEEDRATE { 500, 500, 5, 50 }
//#define LIMITED_MAX_FR_EDITING // Limit edit via M203 or LCD to DEFAULT_MAX_FEEDRATE * 2
#if ENABLED(LIMITED_MAX_FR_EDITING)
#define MAX_FEEDRATE_EDIT_VALUES { 600, 600, 10, 50 } // ...or, set your own edit limits
#endif
/
* Default Max Acceleration (speed change with time) (linear=mm/(s^2), rotational=°/(s^2))
* (Maximum start speed for accelerated moves)
* Override with M201
* X, Y, Z [, I [, J [, K...]]], E0 [, E1[, E2...]]
*/
#define DEFAULT_MAX_ACCELERATION { 500, 500, 100, 1000 }
//#define LIMITED_MAX_ACCEL_EDITING // Limit edit via M201 or LCD to DEFAULT_MAX_ACCELERATION * 2
#if ENABLED(LIMITED_MAX_ACCEL_EDITING)
#define MAX_ACCEL_EDIT_VALUES { 6000, 6000, 200, 20000 } // ...or, set your own edit limits
#endif
/
* Default Acceleration (speed change with time) (linear=mm/(s^2), rotational=°/(s^2))
* Override with M204
*
* M204 P Acceleration
* M204 R Retract Acceleration
* M204 T Travel Acceleration
* M204 I Angular Acceleration
* M204 J Angular Travel Acceleration
*/
#define DEFAULT_ACCELERATION 500 // X, Y, Z ... and E acceleration for printing moves
#define DEFAULT_RETRACT_ACCELERATION 500 // E acceleration for retracts
#define DEFAULT_TRAVEL_ACCELERATION 1500 // X, Y, Z ... acceleration for travel (non printing) moves
#if ENABLED(AXIS4_ROTATES)
#define DEFAULT_ANGULAR_ACCELERATION 3000 // I, J, K acceleration for rotational-only printing moves
#define DEFAULT_ANGULAR_TRAVEL_ACCELERATION 3000 // I, J, K acceleration for rotational-only travel (non printing) moves
#endif
/
* Default Jerk limits (mm/s)
* Override with M205 X Y Z . . . E
*
* "Jerk" specifies the minimum speed change that requires acceleration.
* When changing speed and direction, if the difference is less than the
* value set here, it may happen instantaneously.
*/
#define CLASSIC_JERK
#if ENABLED(CLASSIC_JERK)
#define DEFAULT_XJERK 10.0
#define DEFAULT_YJERK 10.0
#define DEFAULT_ZJERK 0.3
//#define DEFAULT_IJERK 0.3
//#define DEFAULT_JJERK 0.3
//#define DEFAULT_KJERK 0.3
//#define DEFAULT_UJERK 0.3
//#define DEFAULT_VJERK 0.3
//#define DEFAULT_WJERK 0.3
//#define TRAVEL_EXTRA_XYJERK 0.0 // Additional jerk allowance for all travel moves
//#define LIMITED_JERK_EDITING // Limit edit via M205 or LCD to DEFAULT_aJERK * 2
#if ENABLED(LIMITED_JERK_EDITING)
#define MAX_JERK_EDIT_VALUES { 20, 20, 0.6, 10 } // ...or, set your own edit limits
#endif
#endif
#define DEFAULT_EJERK 5.0 // May be used by Linear Advance
Артем, [16.09.2024 16:37]
/
* Junction Deviation Factor
*
* See:
* https://reprap.org/forum/read.php?1,739819
* https://blog.kyneticcnc.com/2018/10/computing-junction-deviation-for-marlin.html
*/
#if DISABLED(CLASSIC_JERK)
#define JUNCTION_DEVIATION_MM 0.013 // (mm) Distance from real junction edge
#define JD_HANDLE_SMALL_SEGMENTS // Use curvature estimation instead of just the junction angle
// for small segments ( 135°).
#endif
/
// For Inverting Stepper Enable Pins (Active Low) use 0, Non Inverting (Active High) use 1
// :{ 0:'Low', 1:'High' }
#define X_ENABLE_ON 0
#define Y_ENABLE_ON 0
#define Z_ENABLE_ON 0
#define E_ENABLE_ON 0 // For all extruders
//#define I_ENABLE_ON 0
//#define J_ENABLE_ON 0
//#define K_ENABLE_ON 0
//#define U_ENABLE_ON 0
//#define V_ENABLE_ON 0
//#define W_ENABLE_ON 0
// Disable axis steppers immediately when they're not being stepped.
// WARNING: When motors turn off there is a chance of losing position accuracy!
#define DISABLE_X false
#define DISABLE_Y false
#define DISABLE_Z false
//#define DISABLE_I false
//#define DISABLE_J false
//#define DISABLE_K false
//#define DISABLE_U false
//#define DISABLE_V false
//#define DISABLE_W false
// Turn off the display blinking that warns about possible accuracy reduction
//#define DISABLE_REDUCED_ACCURACY_WARNING
// @section extruder
#define DISABLE_E false // Disable the extruder when not stepping
#define DISABLE_INACTIVE_EXTRUDER // Keep only the active extruder enabled
// @section motion
// Invert the stepper direction. Change (or reverse the motor connector) if an axis goes the wrong way.
#define INVERT_X_DIR true
#define INVERT_Y_DIR true
#define INVERT_Z_DIR false
//#define INVERT_I_DIR false
//#define INVERT_J_DIR false
//#define INVERT_K_DIR false
//#define INVERT_U_DIR false
//#define INVERT_V_DIR false
//#define INVERT_W_DIR false
// @section extruder
// For direct drive extruder v9 set to true, for geared extruder set to false.
#define INVERT_E0_DIR true
#define INVERT_E1_DIR false
#define INVERT_E2_DIR false
#define INVERT_E3_DIR false
#define INVERT_E4_DIR false
#define INVERT_E5_DIR false
#define INVERT_E6_DIR false
#define INVERT_E7_DIR false
// @section homing
//#define NO_MOTION_BEFORE_HOMING // Inhibit movement until all axes have been homed. Also enable HOME_AFTER_DEACTIVATE for extra safety.
//#define HOME_AFTER_DEACTIVATE // Require rehoming after steppers are deactivated. Also enable NO_MOTION_BEFORE_HOMING for extra safety.
Артем, [16.09.2024 16:37]
/
* Set Z_IDLE_HEIGHT if the Z-Axis moves on its own when steppers are disabled.
* - Use a low value (i.e., Z_MIN_POS) if the nozzle falls down to the bed.
* - Use a large value (i.e., Z_MAX_POS) if the bed falls down, away from the nozzle.
*/
//#define Z_IDLE_HEIGHT Z_HOME_POS
//#define Z_HOMING_HEIGHT 4 // (mm) Minimal Z height before homing (G28) for Z clearance above the bed, clamps, ...
// Be sure to have this much clearance over your Z_MAX_POS to prevent grinding.
//#define Z_AFTER_HOMING 10 // (mm) Height to move to after homing Z
// Direction of endstops when homing; 1=MAX, -1=MIN
// :[-1,1]
#define X_HOME_DIR -1
#define Y_HOME_DIR -1
#define Z_HOME_DIR -1
//#define I_HOME_DIR -1
//#define J_HOME_DIR -1
//#define K_HOME_DIR -1
//#define U_HOME_DIR -1
//#define V_HOME_DIR -1
//#define W_HOME_DIR -1
// @section geometry
// The size of the printable area
#define X_BED_SIZE 220
#define Y_BED_SIZE 220
// Travel limits (linear=mm, rotational=°) after homing, corresponding to endstop positions.
#define X_MIN_POS 0
#define Y_MIN_POS 0
#define Z_MIN_POS 0
#define X_MAX_POS X_BED_SIZE
#define Y_MAX_POS Y_BED_SIZE
#define Z_MAX_POS 235
//#define I_MIN_POS 0
//#define I_MAX_POS 50
//#define J_MIN_POS 0
//#define J_MAX_POS 50
//#define K_MIN_POS 0
//#define K_MAX_POS 50
//#define U_MIN_POS 0
//#define U_MAX_POS 50
//#define V_MIN_POS 0
//#define V_MAX_POS 50
//#define W_MIN_POS 0
//#define W_MAX_POS 50
/
* Software Endstops
*
* - Prevent moves outside the set machine bounds.
* - Individual axes can be disabled, if desired.
* - X and Y only apply to Cartesian robots.
* - Use 'M211' to set software endstops on/off or report current state
*/
// Min software endstops constrain movement within minimum coordinate bounds
#define MIN_SOFTWARE_ENDSTOPS
#if ENABLED(MIN_SOFTWARE_ENDSTOPS)
#define MIN_SOFTWARE_ENDSTOP_X
#define MIN_SOFTWARE_ENDSTOP_Y
#define MIN_SOFTWARE_ENDSTOP_Z
#define MIN_SOFTWARE_ENDSTOP_I
#define MIN_SOFTWARE_ENDSTOP_J
#define MIN_SOFTWARE_ENDSTOP_K
#define MIN_SOFTWARE_ENDSTOP_U
#define MIN_SOFTWARE_ENDSTOP_V
#define MIN_SOFTWARE_ENDSTOP_W
#endif
// Max software endstops constrain movement within maximum coordinate bounds
#define MAX_SOFTWARE_ENDSTOPS
#if ENABLED(MAX_SOFTWARE_ENDSTOPS)
#define MAX_SOFTWARE_ENDSTOP_X
#define MAX_SOFTWARE_ENDSTOP_Y
#define MAX_SOFTWARE_ENDSTOP_Z
#define MAX_SOFTWARE_ENDSTOP_I
#define MAX_SOFTWARE_ENDSTOP_J
#define MAX_SOFTWARE_ENDSTOP_K
#define MAX_SOFTWARE_ENDSTOP_U
#define MAX_SOFTWARE_ENDSTOP_V
#define MAX_SOFTWARE_ENDSTOP_W
#endif
* Configuration_adv.h
*
* Advanced settings.
* Only change these if you know exactly what you're doing.
* Some of these settings can damage your printer if improperly set!
*
* Basic settings can be found in Configuration.h
*/
#define CONFIGURATION_ADV_H_VERSION 02010200
// @section develop
/
* Configuration Export
*
* Export the configuration as part of the build. (See signature.py)
* Output files are saved with the build (e.g., .pio/build/mega2560).
*
* See `build_all_examples --ini` as an example of config.ini archiving.
*
* 1 = marlin_config.json - Dictionary containing the configuration.
* This file is also generated for CONFIGURATION_EMBEDDING.
* 2 = config.ini - File format for PlatformIO preprocessing.
* 3 = schema.json - The entire configuration schema. (13 = pattern groups)
* 4 = schema.yml - The entire configuration schema.
*/
//#define CONFIG_EXPORT 2 // :[1:'JSON', 2:'config.ini', 3:'schema.json', 4:'schema.yml']
//===========================================================================
//============================= Thermal Settings ============================
//===========================================================================
// @section temperature
/
* Thermocouple sensors are quite sensitive to noise. Any noise induced in
* the sensor wires, such as by stepper motor wires run in parallel to them,
* may result in the thermocouple sensor reporting spurious errors. This
* value is the number of errors which can occur in a row before the error
* is reported. This allows us to ignore intermittent error conditions while
* still detecting an actual failure, which should result in a continuous
* stream of errors from the sensor.
*
* Set this value to 0 to fail on the first error to occur.
*/
#define THERMOCOUPLE_MAX_ERRORS 15
//
// Custom Thermistor 1000 parameters
//
#if TEMP_SENSOR_0 == 1000
#define HOTEND0_PULLUP_RESISTOR_OHMS 4700 // Pullup resistor
#define HOTEND0_RESISTANCE_25C_OHMS 100000 // Resistance at 25C
#define HOTEND0_BETA 3950 // Beta value
#define HOTEND0_SH_C_COEFF 0 // Steinhart-Hart C coefficient
#endif
#if TEMP_SENSOR_1 == 1000
#define HOTEND1_PULLUP_RESISTOR_OHMS 4700 // Pullup resistor
#define HOTEND1_RESISTANCE_25C_OHMS 100000 // Resistance at 25C
#define HOTEND1_BETA 3950 // Beta value
#define HOTEND1_SH_C_COEFF 0 // Steinhart-Hart C coefficient
#endif
#if TEMP_SENSOR_2 == 1000
#define HOTEND2_PULLUP_RESISTOR_OHMS 4700 // Pullup resistor
#define HOTEND2_RESISTANCE_25C_OHMS 100000 // Resistance at 25C
#define HOTEND2_BETA 3950 // Beta value
#define HOTEND2_SH_C_COEFF 0 // Steinhart-Hart C coefficient
#endif
#if TEMP_SENSOR_3 == 1000
#define HOTEND3_PULLUP_RESISTOR_OHMS 4700 // Pullup resistor
#define HOTEND3_RESISTANCE_25C_OHMS 100000 // Resistance at 25C
#define HOTEND3_BETA 3950 // Beta value
#define HOTEND3_SH_C_COEFF 0 // Steinhart-Hart C coefficient
#endif
Артем, [16.09.2024 16:46]
#if TEMP_SENSOR_4 == 1000
#define HOTEND4_PULLUP_RESISTOR_OHMS 4700 // Pullup resistor
#define HOTEND4_RESISTANCE_25C_OHMS 100000 // Resistance at 25C
#define HOTEND4_BETA 3950 // Beta value
#define HOTEND4_SH_C_COEFF 0 // Steinhart-Hart C coefficient
#endif
#if TEMP_SENSOR_5 == 1000
#define HOTEND5_PULLUP_RESISTOR_OHMS 4700 // Pullup resistor
#define HOTEND5_RESISTANCE_25C_OHMS 100000 // Resistance at 25C
#define HOTEND5_BETA 3950 // Beta value
#define HOTEND5_SH_C_COEFF 0 // Steinhart-Hart C coefficient
#endif
#if TEMP_SENSOR_6 == 1000
#define HOTEND6_PULLUP_RESISTOR_OHMS 4700 // Pullup resistor
#define HOTEND6_RESISTANCE_25C_OHMS 100000 // Resistance at 25C
#define HOTEND6_BETA 3950 // Beta value
#define HOTEND6_SH_C_COEFF 0 // Steinhart-Hart C coefficient
#endif
#if TEMP_SENSOR_7 == 1000
#define HOTEND7_PULLUP_RESISTOR_OHMS 4700 // Pullup resistor
#define HOTEND7_RESISTANCE_25C_OHMS 100000 // Resistance at 25C
#define HOTEND7_BETA 3950 // Beta value
#define HOTEND7_SH_C_COEFF 0 // Steinhart-Hart C coefficient
#endif
#if TEMP_SENSOR_BED == 1000
#define BED_PULLUP_RESISTOR_OHMS 4700 // Pullup resistor
#define BED_RESISTANCE_25C_OHMS 100000 // Resistance at 25C
#define BED_BETA 3950 // Beta value
#define BED_SH_C_COEFF 0 // Steinhart-Hart C coefficient
#endif
#if TEMP_SENSOR_CHAMBER == 1000
#define CHAMBER_PULLUP_RESISTOR_OHMS 4700 // Pullup resistor
#define CHAMBER_RESISTANCE_25C_OHMS 100000 // Resistance at 25C
#define CHAMBER_BETA 3950 // Beta value
#define CHAMBER_SH_C_COEFF 0 // Steinhart-Hart C coefficient
#endif
#if TEMP_SENSOR_COOLER == 1000
#define COOLER_PULLUP_RESISTOR_OHMS 4700 // Pullup resistor
#define COOLER_RESISTANCE_25C_OHMS 100000 // Resistance at 25C
#define COOLER_BETA 3950 // Beta value
#define COOLER_SH_C_COEFF 0 // Steinhart-Hart C coefficient
#endif
#if TEMP_SENSOR_PROBE == 1000
#define PROBE_PULLUP_RESISTOR_OHMS 4700 // Pullup resistor
#define PROBE_RESISTANCE_25C_OHMS 100000 // Resistance at 25C
#define PROBE_BETA 3950 // Beta value
#define PROBE_SH_C_COEFF 0 // Steinhart-Hart C coefficient
#endif
#if TEMP_SENSOR_BOARD == 1000
#define BOARD_PULLUP_RESISTOR_OHMS 4700 // Pullup resistor
#define BOARD_RESISTANCE_25C_OHMS 100000 // Resistance at 25C
#define BOARD_BETA 3950 // Beta value
#define BOARD_SH_C_COEFF 0 // Steinhart-Hart C coefficient
#endif
#if TEMP_SENSOR_REDUNDANT == 1000
#define REDUNDANT_PULLUP_RESISTOR_OHMS 4700 // Pullup resistor
#define REDUNDANT_RESISTANCE_25C_OHMS 100000 // Resistance at 25C
#define REDUNDANT_BETA 3950 // Beta value
#define REDUNDANT_SH_C_COEFF 0 // Steinhart-Hart C coefficient
#endif
Артем, [16.09.2024 16:46]
/
* Thermocouple Options — for MAX6675 (-2), MAX31855 (-3), and MAX31865 (-5).
*/
//#define TEMP_SENSOR_FORCE_HW_SPI // Ignore SCK/MOSI/MISO pins; use CS and the default SPI bus.
//#define MAX31865_SENSOR_WIRES_0 2 // (2-4) Number of wires for the probe connected to a MAX31865 board.
//#define MAX31865_SENSOR_WIRES_1 2
//#define MAX31865_50HZ_FILTER // Use a 50Hz filter instead of the default 60Hz.
//#define MAX31865_USE_READ_ERROR_DETECTION // Treat value spikes (20°C delta in under 1s) as read errors.
//#define MAX31865_USE_AUTO_MODE // Read faster and more often than 1-shot; bias voltage always on; slight effect on RTD temperature.
//#define MAX31865_MIN_SAMPLING_TIME_MSEC 100 // (ms) 1-shot: minimum read interval. Reduces bias voltage effects by leaving sensor unpowered for longer intervals.
//#define MAX31865_IGNORE_INITIAL_FAULTY_READS 10 // Ignore some read faults (keeping the temperature reading) to work around a possible issue (#23439).
//#define MAX31865_WIRE_OHMS_0 0.95f // For 2-wire, set the wire resistances for more accurate readings.
//#define MAX31865_WIRE_OHMS_1 0.0f
/
* Hephestos 2 24V heated bed upgrade kit.
* https://store.bq.com/en/heated-bed-kit-hephestos2
*/
//#define HEPHESTOS2_HEATED_BED_KIT
#if ENABLED(HEPHESTOS2_HEATED_BED_KIT)
#undef TEMP_SENSOR_BED
#define TEMP_SENSOR_BED 70
#define HEATER_BED_INVERTING true
#endif
//
// Heated Bed Bang-Bang options
//
#if DISABLED(PIDTEMPBED)
#define BED_CHECK_INTERVAL 5000 // (ms) Interval between checks in bang-bang control
#if ENABLED(BED_LIMIT_SWITCHING)
#define BED_HYSTERESIS 2 // (°C) Only set the relevant heater state when ABS(T-target) > BED_HYSTERESIS
#endif
#endif
//
// Heated Chamber options
//
#if DISABLED(PIDTEMPCHAMBER)
#define CHAMBER_CHECK_INTERVAL 5000 // (ms) Interval between checks in bang-bang control
#if ENABLED(CHAMBER_LIMIT_SWITCHING)
#define CHAMBER_HYSTERESIS 2 // (°C) Only set the relevant heater state when ABS(T-target) > CHAMBER_HYSTERESIS
#endif
#endif
#if TEMP_SENSOR_CHAMBER
//#define HEATER_CHAMBER_PIN P2_04 // Required heater on/off pin (example: SKR 1.4 Turbo HE1 plug)
//#define HEATER_CHAMBER_INVERTING false
//#define FAN1_PIN -1 // Remove the fan signal on pin P2_04 (example: SKR 1.4 Turbo HE1 plug)
//#define CHAMBER_FAN // Enable a fan on the chamber
#if ENABLED(CHAMBER_FAN)
//#define CHAMBER_FAN_INDEX 2 // Index of a fan to repurpose as the chamber fan. (Default: first unused fan)
#define CHAMBER_FAN_MODE 2 // Fan control mode: 0=Static; 1=Linear increase when temp is higher than target; 2=V-shaped curve; 3=similar to 1 but fan is always on.
#if CHAMBER_FAN_MODE == 0
#define CHAMBER_FAN_BASE 255 // Chamber fan PWM (0-255)
#elif CHAMBER_FAN_MODE == 1
#define CHAMBER_FAN_BASE 128 // Base chamber fan PWM (0-255); turns on when chamber temperature is above the target
#define CHAMBER_FAN_FACTOR 25 // PWM increase per °C above target
#elif CHAMBER_FAN_MODE == 2
#define CHAMBER_FAN_BASE 128 // Minimum chamber fan PWM (0-255)
#define CHAMBER_FAN_FACTOR 25 // PWM increase per °C difference from target
#elif CHAMBER_FAN_MODE == 3
#define CHAMBER_FAN_BASE 128 // Base chamber fan PWM (0-255)
#define CHAMBER_FAN_FACTOR 25 // PWM increase per °C above target
#endif
#endif
//#define CHAMBER_VENT // Enable a servo-controlled vent on the chamber
#if ENABLED(CHAMBER_VENT)
#define CHAMBER_VENT_SERVO_NR 1 // Index of the vent servo
#define HIGH_EXCESS_HEAT_LIMIT 5 // How much above target temp to consider there is excess heat in the chamber
#define LOW_EXCESS_HEAT_LIMIT 3
#define MIN_COOLING_SLOPE_TIME_CHAMBER_VENT 20
#define MIN_COOLING_SLOPE_DEG_CHAMBER_VENT 1.5
#endif
#endif
Артем, [16.09.2024 16:46]
//
// Laser Cooler options
//
#if TEMP_SENSOR_COOLER
#define COOLER_MINTEMP 8 // (°C)
#define COOLER_MAXTEMP 26 // (°C)
#define COOLER_DEFAULT_TEMP 16 // (°C)
#define TEMP_COOLER_HYSTERESIS 1 // (°C) Temperature proximity considered "close enough" to the target
#define COOLER_PIN 8 // Laser cooler on/off pin used to control power to the cooling element (e.g., TEC, External chiller via relay)
#define COOLER_INVERTING false
#define TEMP_COOLER_PIN 15 // Laser/Cooler temperature sensor pin. ADC is required.
#define COOLER_FAN // Enable a fan on the cooler, Fan# 0,1,2,3 etc.
#define COOLER_FAN_INDEX 0 // FAN number 0, 1, 2 etc. e.g.
#if ENABLED(COOLER_FAN)
#define COOLER_FAN_BASE 100 // Base Cooler fan PWM (0-255); turns on when Cooler temperature is above the target
#define COOLER_FAN_FACTOR 25 // PWM increase per °C above target
#endif
#endif
//
// Motherboard Sensor options
//
#if TEMP_SENSOR_BOARD
#define THERMAL_PROTECTION_BOARD // Halt the printer if the board sensor leaves the temp range below.
#define BOARD_MINTEMP 8 // (°C)
#define BOARD_MAXTEMP 70 // (°C)
#ifndef TEMP_BOARD_PIN
//#define TEMP_BOARD_PIN -1 // Board temp sensor pin, if not set in pins file.
#endif
#endif
/
* Thermal Protection provides additional protection to your printer from damage
* and fire. Marlin always includes safe min and max temperature ranges which
* protect against a broken or disconnected thermistor wire.
*
* The issue: If a thermistor falls out, it will report the much lower
* temperature of the air in the room, and the the firmware will keep
* the heater on.
*
* The solution: Once the temperature reaches the target, start observing.
* If the temperature stays too far below the target (hysteresis) for too
* long (period), the firmware will halt the machine as a safety precaution.
*
* If you get false positives for "Thermal Runaway", increase
* THERMAL_PROTECTION_HYSTERESIS and/or THERMAL_PROTECTION_PERIOD
*/
#if ENABLED(THERMAL_PROTECTION_HOTENDS)
#define THERMAL_PROTECTION_PERIOD 40 // Seconds
#define THERMAL_PROTECTION_HYSTERESIS 4 // Degrees Celsius
//#define ADAPTIVE_FAN_SLOWING // Slow part cooling fan if temperature drops
#if BOTH(ADAPTIVE_FAN_SLOWING, PIDTEMP)
//#define NO_FAN_SLOWING_IN_PID_TUNING // Don't slow fan speed during M303
#endif
/
* Whenever an M104, M109, or M303 increases the target temperature, the
* firmware will wait for the WATCH_TEMP_PERIOD to expire. If the temperature
* hasn't increased by WATCH_TEMP_INCREASE degrees, the machine is halted and
* requires a hard reset. This test restarts with any M104/M109/M303, but only
* if the current temperature is far enough below the target for a reliable
* test.
*
* If you get false positives for "Heating failed", increase WATCH_TEMP_PERIOD
* and/or decrease WATCH_TEMP_INCREASE. WATCH_TEMP_INCREASE should not be set
* below 2.
*/
#define WATCH_TEMP_PERIOD 40 // Seconds
#define WATCH_TEMP_INCREASE 2 // Degrees Celsius
#endif
/
* Thermal Protection parameters for the bed are just as above for hotends.
*/
#if ENABLED(THERMAL_PROTECTION_BED)
#define THERMAL_PROTECTION_BED_PERIOD 20 // Seconds
#define THERMAL_PROTECTION_BED_HYSTERESIS 2 // Degrees Celsius
/
* As described above, except for the bed (M140/M190/M303).
*/
#define WATCH_BED_TEMP_PERIOD 60 // Seconds
#define WATCH_BED_TEMP_INCREASE 2 // Degrees Celsius
#endif
Артем, [16.09.2024 16:46]
/
* Thermal Protection parameters for the heated chamber.
*/
#if ENABLED(THERMAL_PROTECTION_CHAMBER)
#define THERMAL_PROTECTION_CHAMBER_PERIOD 20 // Seconds
#define THERMAL_PROTECTION_CHAMBER_HYSTERESIS 2 // Degrees Celsius
/
* Heated chamber watch settings (M141/M191).
*/
#define WATCH_CHAMBER_TEMP_PERIOD 60 // Seconds
#define WATCH_CHAMBER_TEMP_INCREASE 2 // Degrees Celsius
#endif
/
* Thermal Protection parameters for the laser cooler.
*/
#if ENABLED(THERMAL_PROTECTION_COOLER)
#define THERMAL_PROTECTION_COOLER_PERIOD 10 // Seconds
#define THERMAL_PROTECTION_COOLER_HYSTERESIS 3 // Degrees Celsius
/
* Laser cooling watch settings (M143/M193).
*/
#define WATCH_COOLER_TEMP_PERIOD 60 // Seconds
#define WATCH_COOLER_TEMP_INCREASE 3 // Degrees Celsius
#endif
#if ANY(THERMAL_PROTECTION_HOTENDS, THERMAL_PROTECTION_BED, THERMAL_PROTECTION_CHAMBER, THERMAL_PROTECTION_COOLER)
/
* Thermal Protection Variance Monitor - EXPERIMENTAL.
* Kill the machine on a stuck temperature sensor. Disable if you get false positives.
*/
//#define THERMAL_PROTECTION_VARIANCE_MONITOR // Detect a sensor malfunction preventing temperature updates
#endif
#if ENABLED(PIDTEMP)
// Add an experimental additional term to the heater power, proportional to the extrusion speed.
// A well-chosen Kc value should add just enough power to melt the increased material volume.
//#define PID_EXTRUSION_SCALING
#if ENABLED(PID_EXTRUSION_SCALING)
#define DEFAULT_Kc (100) // heating power = Kc * e_speed
#define LPQ_MAX_LEN 50
#endif
/
* Add an experimental additional term to the heater power, proportional to the fan speed.
* A well-chosen Kf value should add just enough power to compensate for power-loss from the cooling fan.
* You can either just add a constant compensation with the DEFAULT_Kf value
* or follow the instruction below to get speed-dependent compensation.
*
* Constant compensation (use only with fanspeeds of 0% and 100%)
* ---------------------------------------------------------------------
* A good starting point for the Kf-value comes from the calculation:
* kf = (power_fan * eff_fan) / power_heater * 255
* where eff_fan is between 0.0 and 1.0, based on fan-efficiency and airflow to the nozzle / heater.
*
* Example:
* Heater: 40W, Fan: 0.1A * 24V = 2.4W, eff_fan = 0.8
* Kf = (2.4W * 0.8) / 40W * 255 = 12.24
*
* Fan-speed dependent compensation
* --------------------------------
* 1. To find a good Kf value, set the hotend temperature, wait for it to settle, and enable the fan (100%).
* Make sure PID_FAN_SCALING_LIN_FACTOR is 0 and PID_FAN_SCALING_ALTERNATIVE_DEFINITION is not enabled.
* If you see the temperature drop repeat the test, increasing the Kf value slowly, until the temperature
* drop goes away. If the temperature overshoots after enabling the fan, the Kf value is too big.
* 2. Note the Kf-value for fan-speed at 100%
* 3. Determine a good value for PID_FAN_SCALING_MIN_SPEED, which is around the speed, where the fan starts moving.
* 4. Repeat step 1. and 2. for this fan speed.
* 5. Enable PID_FAN_SCALING_ALTERNATIVE_DEFINITION and enter the two identified Kf-values in
* PID_FAN_SCALING_AT_FULL_SPEED and PID_FAN_SCALING_AT_MIN_SPEED. Enter the minimum speed in PID_FAN_SCALING_MIN_SPEED
*/
//#define PID_FAN_SCALING
#if ENABLED(PID_FAN_SCALING)
//#define PID_FAN_SCALING_ALTERNATIVE_DEFINITION
#if ENABLED(PID_FAN_SCALING_ALTERNATIVE_DEFINITION)
// The alternative definition is used for an easier configuration.
// Just figure out Kf at fullspeed (255) and PID_FAN_SCALING_MIN_SPEED.
// DEFAULT_Kf and PID_FAN_SCALING_LIN_FACTOR are calculated accordingly.
Артем, [16.09.2024 16:46]
#define PID_FAN_SCALING_AT_FULL_SPEED 13.0 //=PID_FAN_SCALING_LIN_FACTOR*255+DEFAULT_Kf
#define PID_FAN_SCALING_AT_MIN_SPEED 6.0 //=PID_FAN_SCALING_LIN_FACTOR*PID_FAN_SCALING_MIN_SPEED+DEFAULT_Kf
#define PID_FAN_SCALING_MIN_SPEED 10.0 // Minimum fan speed at which to enable PID_FAN_SCALING
#define DEFAULT_Kf (255.0*PID_FAN_SCALING_AT_MIN_SPEED-PID_FAN_SCALING_AT_FULL_SPEED*PID_FAN_SCALING_MIN_SPEED)/(255.0-PID_FAN_SCALING_MIN_SPEED)
#define PID_FAN_SCALING_LIN_FACTOR (PID_FAN_SCALING_AT_FULL_SPEED-DEFAULT_Kf)/255.0
#else
#define PID_FAN_SCALING_LIN_FACTOR (0) // Power loss due to cooling = Kf * (fan_speed)
#define DEFAULT_Kf 10 // A constant value added to the PID-tuner
#define PID_FAN_SCALING_MIN_SPEED 10 // Minimum fan speed at which to enable PID_FAN_SCALING
#endif
#endif
#endif
/
* Automatic Temperature Mode
*
* Dynamically adjust the hotend target temperature based on planned E moves.
*
* (Contrast with PID_EXTRUSION_SCALING, which tracks E movement and adjusts PID
* behavior using an additional kC value.)
*
* Autotemp is calculated by (mintemp + factor * mm_per_sec), capped to maxtemp.
*
* Enable Autotemp Mode with M104/M109 F S B.
* Disable by sending M104/M109 with no F parameter (or F0 with AUTOTEMP_PROPORTIONAL).
*/
#define AUTOTEMP
#if ENABLED(AUTOTEMP)
#define AUTOTEMP_OLDWEIGHT 0.98 // Factor used to weight previous readings (0.0 0 in the constants below
*/
// The number of consecutive low temperature errors that can occur
// before a min_temp_error is triggered. (Shouldn't be more than 10.)
//#define MAX_CONSECUTIVE_LOW_TEMPERATURE_ERROR_ALLOWED 0
/
* The number of milliseconds a hotend will preheat before starting to check
* the temperature. This value should NOT be set to the time it takes the
* hot end to reach the target temperature, but the time it takes to reach
* the minimum temperature your thermistor can read. The lower the better/safer.
* This shouldn't need to be more than 30 seconds (30000)
*/
//#define MILLISECONDS_PREHEAT_TIME 0
// @section extruder
/
* Extruder runout prevention.
* If the machine is idle and the temperature over MINTEMP
* then extrude some filament every couple of SECONDS.
*/
//#define EXTRUDER_RUNOUT_PREVENT
#if ENABLED(EXTRUDER_RUNOUT_PREVENT)
#define EXTRUDER_RUNOUT_MINTEMP 190
#define EXTRUDER_RUNOUT_SECONDS 30
#define EXTRUDER_RUNOUT_SPEED 1500 // (mm/min)
#define EXTRUDER_RUNOUT_EXTRUDE 5 // (mm)
#endif
Артем, [16.09.2024 16:46]
/
* Hotend Idle Timeout
* Prevent filament in the nozzle from charring and causing a critical jam.
*/
//#define HOTEND_IDLE_TIMEOUT
#if ENABLED(HOTEND_IDLE_TIMEOUT)
#define HOTEND_IDLE_TIMEOUT_SEC (5*60) // (seconds) Time without extruder movement to trigger protection
#define HOTEND_IDLE_MIN_TRIGGER 180 // (°C) Minimum temperature to enable hotend protection
#define HOTEND_IDLE_NOZZLE_TARGET 0 // (°C) Safe temperature for the nozzle after timeout
#define HOTEND_IDLE_BED_TARGET 0 // (°C) Safe temperature for the bed after timeout
#endif
// @section temperature
// Calibration for AD595 / AD8495 sensor to adjust temperature measurements.
// The final temperature is calculated as (measuredTemp * GAIN) + OFFSET.
#define TEMP_SENSOR_AD595_OFFSET 0.0
#define TEMP_SENSOR_AD595_GAIN 1.0
#define TEMP_SENSOR_AD8495_OFFSET 0.0
#define TEMP_SENSOR_AD8495_GAIN 1.0
/
* Controller Fan
* To cool down the stepper drivers and MOSFETs.
*
* The fan turns on automatically whenever any driver is enabled and turns
* off (or reduces to idle speed) shortly after drivers are turned off.
*/
//#define USE_CONTROLLER_FAN
#if ENABLED(USE_CONTROLLER_FAN)
//#define CONTROLLER_FAN_PIN -1 // Set a custom pin for the controller fan
//#define CONTROLLER_FAN_USE_Z_ONLY // With this option only the Z axis is considered
//#define CONTROLLER_FAN_IGNORE_Z // Ignore Z stepper. Useful when stepper timeout is disabled.
#define CONTROLLERFAN_SPEED_MIN 0 // (0-255) Minimum speed. (If set below this value the fan is turned off.)
#define CONTROLLERFAN_SPEED_ACTIVE 255 // (0-255) Active speed, used when any motor is enabled
#define CONTROLLERFAN_SPEED_IDLE 0 // (0-255) Idle speed, used when motors are disabled
#define CONTROLLERFAN_IDLE_TIME 60 // (seconds) Extra time to keep the fan running after disabling motors
// Use TEMP_SENSOR_BOARD as a trigger for enabling the controller fan
//#define CONTROLLER_FAN_MIN_BOARD_TEMP 40 // (°C) Turn on the fan if the board reaches this temperature
//#define CONTROLLER_FAN_EDITABLE // Enable M710 configurable settings
#if ENABLED(CONTROLLER_FAN_EDITABLE)
#define CONTROLLER_FAN_MENU // Enable the Controller Fan submenu
#endif
#endif
// When first starting the main fan, run it at full speed for the
// given number of milliseconds. This gets the fan spinning reliably
// before setting a PWM value. (Does not work with software PWM for fan on Sanguinololu)
//#define FAN_KICKSTART_TIME 100
// Some coolers may require a non-zero "off" state.
//#define FAN_OFF_PWM 1
Артем, [16.09.2024 16:46]
/
* PWM Fan Scaling
*
* Define the min/max speeds for PWM fans (as set with M106).
*
* With these options the M106 0-255 value range is scaled to a subset
* to ensure that the fan has enough power to spin, or to run lower
* current fans with higher current. (e.g., 5V/12V fans with 12V/24V)
* Value 0 always turns off the fan.
*
* Define one or both of these to override the default 0-255 range.
*/
//#define FAN_MIN_PWM 50
//#define FAN_MAX_PWM 128
/
* Fan Fast PWM
*
* Combinations of PWM Modes, prescale values and TOP resolutions are used internally
* to produce a frequency as close as possible to the desired frequency.
*
* FAST_PWM_FAN_FREQUENCY
* Set this to your desired frequency.
* For AVR, if left undefined this defaults to F = F_CPU/(2*255*1)
* i.e., F = 31.4kHz on 16MHz microcontrollers or F = 39.2kHz on 20MHz microcontrollers.
* For non AVR, if left undefined this defaults to F = 1Khz.
* This F value is only to protect the hardware from an absence of configuration
* and not to complete it when users are not aware that the frequency must be specifically set to support the target board.
*
* NOTE: Setting very low frequencies (:
*
* 0 : (FULL_CONTROL) The slicer has full control over both X-carriages and can achieve optimal travel
* results as long as it supports dual X-carriages. (M605 S0)
*
* 1 : (AUTO_PARK) The firmware automatically parks and unparks the X-carriages on tool-change so
* that additional slicer support is not required. (M605 S1)
*
Артем, [16.09.2024 16:46]
* 2 : (DUPLICATION) The firmware moves the second X-carriage and extruder in synchronization with
* the first X-carriage and extruder, to print 2 copies of the same object at the same time.
* Set the constant X-offset and temperature differential with M605 S2 X[offs] R[deg] and
* follow with M605 S2 to initiate duplicated movement.
*
* 3 : (MIRRORED) Formbot/Vivedino-inspired mirrored mode in which the second extruder duplicates
* the movement of the first except the second extruder is reversed in the X axis.
* Set the initial X offset and temperature differential with M605 S2 X[offs] R[deg] and
* follow with M605 S3 to initiate mirrored movement.
*/
//#define DUAL_X_CARRIAGE
#if ENABLED(DUAL_X_CARRIAGE)
#define X1_MIN_POS X_MIN_POS // Set to X_MIN_POS
#define X1_MAX_POS X_BED_SIZE // A max coordinate so the X1 carriage can't hit the parked X2 carriage
#define X2_MIN_POS 80 // A min coordinate so the X2 carriage can't hit the parked X1 carriage
#define X2_MAX_POS 353 // The max position of the X2 carriage, typically also the home position
#define X2_HOME_DIR 1 // Set to 1. The X2 carriage always homes to the max endstop position
#define X2_HOME_POS X2_MAX_POS // Default X2 home position. Set to X2_MAX_POS.
// NOTE: For Dual X Carriage use M218 T1 Xn to override the X2_HOME_POS.
// This allows recalibration of endstops distance without a rebuild.
// Remember to set the second extruder's X-offset to 0 in your slicer.
// This is the default power-up mode which can be changed later using M605 S.
#define DEFAULT_DUAL_X_CARRIAGE_MODE DXC_AUTO_PARK_MODE
// Default x offset in duplication mode (typically set to half print bed width)
#define DEFAULT_DUPLICATION_X_OFFSET 100
// Default action to execute following M605 mode change commands. Typically G28X to apply new mode.
//#define EVENT_GCODE_IDEX_AFTER_MODECHANGE "G28X"
#endif
Артем, [16.09.2024 16:46]
/
* Multi-Stepper / Multi-Endstop
*
* When X2_DRIVER_TYPE is defined, this indicates that the X and X2 motors work in tandem.
* The following explanations for X also apply to Y and Z multi-stepper setups.
* Endstop offsets may be changed by 'M666 X Y Z' and stored to EEPROM.
*
* - Enable INVERT_X2_VS_X_DIR if the X2 motor requires an opposite DIR signal from X.
*
* - Enable X_DUAL_ENDSTOPS if the second motor has its own endstop, with adjustable offset.
*
* - Extra endstops are included in the output of 'M119'.
*
* - Set X_DUAL_ENDSTOP_ADJUSTMENT to the known error in the X2 endstop.
* Applied to the X2 motor on 'G28' / 'G28 X'.
* Get the offset by homing X and measuring the error.
* Also set with 'M666 X' and stored to EEPROM with 'M500'.
*
* - Use X2_USE_ENDSTOP to set the endstop plug by name. (_XMIN_, _XMAX_, _YMIN_, _YMAX_, _ZMIN_, _ZMAX_)
*/
#if HAS_X2_STEPPER && DISABLED(DUAL_X_CARRIAGE)
//#define INVERT_X2_VS_X_DIR // X2 direction signal is the opposite of X
//#define X_DUAL_ENDSTOPS // X2 has its own endstop
#if ENABLED(X_DUAL_ENDSTOPS)
#define X2_USE_ENDSTOP _XMAX_ // X2 endstop board plug. Don't forget to enable USE_*_PLUG.
#define X2_ENDSTOP_ADJUSTMENT 0 // X2 offset relative to X endstop
#endif
#endif
#if HAS_DUAL_Y_STEPPERS
//#define INVERT_Y2_VS_Y_DIR // Y2 direction signal is the opposite of Y
//#define Y_DUAL_ENDSTOPS // Y2 has its own endstop
#if ENABLED(Y_DUAL_ENDSTOPS)
#define Y2_USE_ENDSTOP _YMAX_ // Y2 endstop board plug. Don't forget to enable USE_*_PLUG.
#define Y2_ENDSTOP_ADJUSTMENT 0 // Y2 offset relative to Y endstop
#endif
#endif
//
// Multi-Z steppers
//
#ifdef Z2_DRIVER_TYPE
//#define INVERT_Z2_VS_Z_DIR // Z2 direction signal is the opposite of Z
//#define Z_MULTI_ENDSTOPS // Other Z axes have their own endstops
#if ENABLED(Z_MULTI_ENDSTOPS)
#define Z2_USE_ENDSTOP _XMAX_ // Z2 endstop board plug. Don't forget to enable USE_*_PLUG.
#define Z2_ENDSTOP_ADJUSTMENT 0 // Z2 offset relative to Y endstop
#endif
#ifdef Z3_DRIVER_TYPE
//#define INVERT_Z3_VS_Z_DIR // Z3 direction signal is the opposite of Z
#if ENABLED(Z_MULTI_ENDSTOPS)
#define Z3_USE_ENDSTOP _YMAX_ // Z3 endstop board plug. Don't forget to enable USE_*_PLUG.
#define Z3_ENDSTOP_ADJUSTMENT 0 // Z3 offset relative to Y endstop
#endif
#endif
#ifdef Z4_DRIVER_TYPE
//#define INVERT_Z4_VS_Z_DIR // Z4 direction signal is the opposite of Z
#if ENABLED(Z_MULTI_ENDSTOPS)
#define Z4_USE_ENDSTOP _ZMAX_ // Z4 endstop board plug. Don't forget to enable USE_*_PLUG.
#define Z4_ENDSTOP_ADJUSTMENT 0 // Z4 offset relative to Y endstop
#endif
#endif
#endif
// Drive the E axis with two synchronized steppers
//#define E_DUAL_STEPPER_DRIVERS
#if ENABLED(E_DUAL_STEPPER_DRIVERS)
//#define INVERT_E1_VS_E0_DIR // E direction signals are opposites
#endif
// Activate a solenoid on the active extruder with M380. Disable all with M381.
// Define SOL0_PIN, SOL1_PIN, etc., for each extruder that has a solenoid.
//#define EXT_SOLENOID
// @section homing
/
* Homing Procedure
* Homing (G28) does an indefinite move towards the endstops to establish
* the position of the toolhead relative to the workspace.
*/
//#define SENSORLESS_BACKOFF_MM { 2, 2, 0 } // (linear=mm, rotational=°) Backoff from endstops before sensorless homing
#define HOMING_BUMP_MM { 5, 5, 2 } // (linear=mm, rotational=°) Backoff from endstops after first bump
#define HOMING_BUMP_DIVISOR { 2, 2, 4 } // Re-Bump Speed Divisor (Divides the Homing Feedrate)
//#define HOMING_BACKOFF_POST_MM { 2, 2, 2 } // (linear=mm, rotational=°) Backoff from endstops after homing
//#define XY_COUNTERPART_BACKOFF_MM 0 // (mm) Backoff X after homing Y, and vice-versa
Артем, [16.09.2024 16:46]
//#define QUICK_HOME // If G28 contains XY do a diagonal move first
//#define HOME_Y_BEFORE_X // If G28 contains XY home Y before X
//#define HOME_Z_FIRST // Home Z first. Requires a Z-MIN endstop (not a probe).
//#define CODEPENDENT_XY_HOMING // If X/Y can't home without homing Y/X first
// @section bltouch
#if ENABLED(BLTOUCH)
/
* Either: Use the defaults (recommended) or: For special purposes, use the following DEFINES
* Do not activate settings that the probe might not understand. Clones might misunderstand
* advanced commands.
*
* Note: If the probe is not deploying, do a "Reset" and "Self-Test" and then check the
* wiring of the BROWN, RED and ORANGE wires.
*
* Note: If the trigger signal of your probe is not being recognized, it has been very often
* because the BLACK and WHITE wires needed to be swapped. They are not "interchangeable"
* like they would be with a real switch. So please check the wiring first.
*
* Settings for all BLTouch and clone probes:
*/
// Safety: The probe needs time to recognize the command.
// Minimum command delay (ms). Enable and increase if needed.
//#define BLTOUCH_DELAY 500
/
* Settings for BLTOUCH Classic 1.2, 1.3 or BLTouch Smart 1.0, 2.0, 2.2, 3.0, 3.1, and most clones:
*/
// Feature: Switch into SW mode after a deploy. It makes the output pulse longer. Can be useful
// in special cases, like noisy or filtered input configurations.
//#define BLTOUCH_FORCE_SW_MODE
/
* Settings for BLTouch Smart 3.0 and 3.1
* Summary:
* - Voltage modes: 5V and OD (open drain - "logic voltage free") output modes
* - High-Speed mode
* - Disable LCD voltage options
*/
/
* Danger: Don't activate 5V mode unless attached to a 5V-tolerant controller!
* V3.0 or 3.1: Set default mode to 5V mode at Marlin startup.
* If disabled, OD mode is the hard-coded default on 3.0
* On startup, Marlin will compare its eeprom to this value. If the selected mode
* differs, a mode set eeprom write will be completed at initialization.
* Use the option below to force an eeprom write to a V3.1 probe regardless.
*/
//#define BLTOUCH_SET_5V_MODE
/
* Safety: Activate if connecting a probe with an unknown voltage mode.
* V3.0: Set a probe into mode selected above at Marlin startup. Required for 5V mode on 3.0
* V3.1: Force a probe with unknown mode into selected mode at Marlin startup ( = Probe EEPROM write )
* To preserve the life of the probe, use this once then turn it off and re-flash.
*/
//#define BLTOUCH_FORCE_MODE_SET
/
* Enable "HIGH SPEED" option for probing.
* Danger: Disable if your probe sometimes fails. Only suitable for stable well-adjusted systems.
* This feature was designed for Deltabots with very fast Z moves; however, higher speed Cartesians
* might be able to use it. If the machine can't raise Z fast enough the BLTouch may go into ALARM.
*
* Set the default state here, change with 'M401 S' or UI, use M500 to save, M502 to reset.
*/
//#define BLTOUCH_HS_MODE true
// Safety: Enable voltage mode settings in the LCD menu.
//#define BLTOUCH_LCD_VOLTAGE_MENU
#endif // BLTOUCH
// @section extras
/
* Z Steppers Auto-Alignment
* Add the G34 command to align multiple Z steppers using a bed probe.
*/
//#define Z_STEPPER_AUTO_ALIGN
#if ENABLED(Z_STEPPER_AUTO_ALIGN)
/
* Define probe X and Y positions for Z1, Z2 [, Z3 [, Z4]]
* These positions are machine-relative and do not shift with the M206 home offset!
* If not defined, probe limits will be used.
* Override with 'M422 S X Y'.
*/
//#define Z_STEPPER_ALIGN_XY { { 10, 190 }, { 100, 10 }, { 190, 190 } }
Артем, [16.09.2024 16:46]
/
* Orientation for the automatically-calculated probe positions.
* Override Z stepper align points with 'M422 S X Y'
*
* 2 Steppers: (0) (1)
* | | 2 |
* | 1 2 | |
* | | 1 |
*
* 3 Steppers: (0) (1) (2) (3)
* | 3 | 1 | 2 1 | 2 |
* | | 3 | | 3 |
* | 1 2 | 2 | 3 | 1 |
*
* 4 Steppers: (0) (1) (2) (3)
* | 4 3 | 1 4 | 2 1 | 3 2 |
* | | | | |
* | 1 2 | 2 3 | 3 4 | 4 1 |
*/
#ifndef Z_STEPPER_ALIGN_XY
//#define Z_STEPPERS_ORIENTATION 0
#endif
/
* Z Stepper positions for more rapid convergence in bed alignment.
* Requires 3 or 4 Z steppers.
*
* Define Stepper XY positions for Z1, Z2, Z3... corresponding to the screw
* positions in the bed carriage, with one position per Z stepper in stepper
* driver order.
*/
//#define Z_STEPPER_ALIGN_STEPPER_XY { { 210.7, 102.5 }, { 152.6, 220.0 }, { 94.5, 102.5 } }
#ifndef Z_STEPPER_ALIGN_STEPPER_XY
// Amplification factor. Used to scale the correction step up or down in case
// the stepper (spindle) position is farther out than the test point.
#define Z_STEPPER_ALIGN_AMP 1.0 // Use a value > 1.0 NOTE: This may cause instability!
#endif
// On a 300mm bed a 5% grade would give a misalignment of ~1.5cm
#define G34_MAX_GRADE 5 // (%) Maximum incline that G34 will handle
#define Z_STEPPER_ALIGN_ITERATIONS 5 // Number of iterations to apply during alignment
#define Z_STEPPER_ALIGN_ACC 0.02 // Stop iterating early if the accuracy is better than this
#define RESTORE_LEVELING_AFTER_G34 // Restore leveling after G34 is done?
// After G34, re-home Z (G28 Z) or just calculate it from the last probe heights?
// Re-homing might be more precise in reproducing the actual 'G28 Z' homing height, especially on an uneven bed.
#define HOME_AFTER_G34
#endif
//
// Add the G35 command to read bed corners to help adjust screws. Requires a bed probe.
//
//#define ASSISTED_TRAMMING
#if ENABLED(ASSISTED_TRAMMING)
// Define positions for probe points.
#define TRAMMING_POINT_XY { { 20, 20 }, { 180, 20 }, { 180, 180 }, { 20, 180 } }
// Define position names for probe points.
#define TRAMMING_POINT_NAME_1 "Front-Left"
#define TRAMMING_POINT_NAME_2 "Front-Right"
#define TRAMMING_POINT_NAME_3 "Back-Right"
#define TRAMMING_POINT_NAME_4 "Back-Left"
#define RESTORE_LEVELING_AFTER_G35 // Enable to restore leveling setup after operation
//#define REPORT_TRAMMING_MM // Report Z deviation (mm) for each point relative to the first
//#define ASSISTED_TRAMMING_WIZARD // Add a Tramming Wizard to the LCD menu
//#define ASSISTED_TRAMMING_WAIT_POSITION { X_CENTER, Y_CENTER, 30 } // Move the nozzle out of the way for adjustment
Артем, [16.09.2024 16:46]
/
* Screw thread:
* M3: 30 = Clockwise, 31 = Counter-Clockwise
* M4: 40 = Clockwise, 41 = Counter-Clockwise
* M5: 50 = Clockwise, 51 = Counter-Clockwise
*/
#define TRAMMING_SCREW_THREAD 30
#endif
// @section motion
#define AXIS_RELATIVE_MODES { false, false, false, false }
// Add a Duplicate option for well-separated conjoined nozzles
//#define MULTI_NOZZLE_DUPLICATION
// By default pololu step drivers require an active high signal. However, some high power drivers require an active low signal as step.
#define INVERT_X_STEP_PIN false
#define INVERT_Y_STEP_PIN false
#define INVERT_Z_STEP_PIN false
#define INVERT_I_STEP_PIN false
#define INVERT_J_STEP_PIN false
#define INVERT_K_STEP_PIN false
#define INVERT_U_STEP_PIN false
#define INVERT_V_STEP_PIN false
#define INVERT_W_STEP_PIN false
#define INVERT_E_STEP_PIN false
/
* Idle Stepper Shutdown
* Set DISABLE_INACTIVE_? 'true' to shut down axis steppers after an idle period.
* The Deactive Time can be overridden with M18 and M84. Set to 0 for No Timeout.
*/
#define DEFAULT_STEPPER_DEACTIVE_TIME 120
#define DISABLE_INACTIVE_X true
#define DISABLE_INACTIVE_Y true
#define DISABLE_INACTIVE_Z true // Set 'false' if the nozzle could fall onto your printed part!
#define DISABLE_INACTIVE_I true
#define DISABLE_INACTIVE_J true
#define DISABLE_INACTIVE_K true
#define DISABLE_INACTIVE_U true
#define DISABLE_INACTIVE_V true
#define DISABLE_INACTIVE_W true
#define DISABLE_INACTIVE_E true
// Default Minimum Feedrates for printing and travel moves
#define DEFAULT_MINIMUMFEEDRATE 0.0 // (mm/s. °/s for rotational-only moves) Minimum feedrate. Set with M205 S.
#define DEFAULT_MINTRAVELFEEDRATE 0.0 // (mm/s. °/s for rotational-only moves) Minimum travel feedrate. Set with M205 T.
// Minimum time that a segment needs to take as the buffer gets emptied
#define DEFAULT_MINSEGMENTTIME 20000 // (µs) Set with M205 B.
// Slow down the machine if the lookahead buffer is (by default) half full.
// Increase the slowdown divisor for larger buffer sizes.
#define SLOWDOWN
#if ENABLED(SLOWDOWN)
#define SLOWDOWN_DIVISOR 2
#endif
Артем, [16.09.2024 16:46]
/
* XY Frequency limit
* Reduce resonance by limiting the frequency of small zigzag infill moves.
* See https://hydraraptor.blogspot.com/2010/12/frequency-limit.html
* Use M201 F G to change limits at runtime.
*/
//#define XY_FREQUENCY_LIMIT 10 // (Hz) Maximum frequency of small zigzag infill moves. Set with M201 F.
#ifdef XY_FREQUENCY_LIMIT
#define XY_FREQUENCY_MIN_PERCENT 5 // (percent) Minimum FR percentage to apply. Set with M201 G.
#endif
// Minimum planner junction speed. Sets the default minimum speed the planner plans for at the end
// of the buffer and all stops. This should not be much greater than zero and should only be changed
// if unwanted behavior is observed on a user's machine when running at very slow speeds.
#define MINIMUM_PLANNER_SPEED 0.05 // (mm/s)
//
// Backlash Compensation
// Adds extra movement to axes on direction-changes to account for backlash.
//
//#define BACKLASH_COMPENSATION
#if ENABLED(BACKLASH_COMPENSATION)
// Define values for backlash distance and correction.
// If BACKLASH_GCODE is enabled these values are the defaults.
#define BACKLASH_DISTANCE_MM { 0, 0, 0 } // (linear=mm, rotational=°) One value for each linear axis
#define BACKLASH_CORRECTION 0.0 // 0.0 = no correction; 1.0 = full correction
// Add steps for motor direction changes on CORE kinematics
//#define CORE_BACKLASH
// Set BACKLASH_SMOOTHING_MM to spread backlash correction over multiple segments
// to reduce print artifacts. (Enabling this is costly in memory and computation!)
//#define BACKLASH_SMOOTHING_MM 3 // (mm)
// Add runtime configuration and tuning of backlash values (M425)
//#define BACKLASH_GCODE
#if ENABLED(BACKLASH_GCODE)
// Measure the Z backlash when probing (G29) and set with "M425 Z"
#define MEASURE_BACKLASH_WHEN_PROBING
#if ENABLED(MEASURE_BACKLASH_WHEN_PROBING)
// When measuring, the probe will move up to BACKLASH_MEASUREMENT_LIMIT
// mm away from point of contact in BACKLASH_MEASUREMENT_RESOLUTION
// increments while checking for the contact to be broken.
#define BACKLASH_MEASUREMENT_LIMIT 0.5 // (mm)
#define BACKLASH_MEASUREMENT_RESOLUTION 0.005 // (mm)
#define BACKLASH_MEASUREMENT_FEEDRATE Z_PROBE_FEEDRATE_SLOW // (mm/min)
#endif
#endif
#endif
/
* Automatic backlash, position and hotend offset calibration
*
* Enable G425 to run automatic calibration using an electrically-
* conductive cube, bolt, or washer mounted on the bed.
*
* G425 uses the probe to touch the top and sides of the calibration object
* on the bed and measures and/or correct positional offsets, axis backlash
* and hotend offsets.
*
* Note: HOTEND_OFFSET and CALIBRATION_OBJECT_CENTER must be set to within
* ±5mm of true values for G425 to succeed.
*/
//#define CALIBRATION_GCODE
#if ENABLED(CALIBRATION_GCODE)
//#define CALIBRATION_SCRIPT_PRE "M117 Starting Auto-Calibration\nT0\nG28\nG12\nM117 Calibrating..."
//#define CALIBRATION_SCRIPT_POST "M500\nM117 Calibration data saved"
#define CALIBRATION_MEASUREMENT_RESOLUTION 0.01 // mm
#define CALIBRATION_FEEDRATE_SLOW 60 // mm/min
#define CALIBRATION_FEEDRATE_FAST 1200 // mm/min
#define CALIBRATION_FEEDRATE_TRAVEL 3000 // mm/min
// The following parameters refer to the conical section of the nozzle tip.
#define CALIBRATION_NOZZLE_TIP_HEIGHT 1.0 // mm
#define CALIBRATION_NOZZLE_OUTER_DIAMETER 2.0 // mm
// Uncomment to enable reporting (required for "G425 V", but consumes PROGMEM).
//#define CALIBRATION_REPORTING
// The true location and dimension the cube/bolt/washer on the bed.
#define CALIBRATION_OBJECT_CENTER { 264.0, -22.0, -2.0 } // mm
#define CALIBRATION_OBJECT_DIMENSIONS { 10.0, 10.0, 10.0 } // mm
Артем, [16.09.2024 16:46]
// Comment out any sides which are unreachable by the probe. For best
// auto-calibration results, all sides must be reachable.
#define CALIBRATION_MEASURE_RIGHT
#define CALIBRATION_MEASURE_FRONT
#define CALIBRATION_MEASURE_LEFT
#define CALIBRATION_MEASURE_BACK
//#define CALIBRATION_MEASURE_IMIN
//#define CALIBRATION_MEASURE_IMAX
//#define CALIBRATION_MEASURE_JMIN
//#define CALIBRATION_MEASURE_JMAX
//#define CALIBRATION_MEASURE_KMIN
//#define CALIBRATION_MEASURE_KMAX
//#define CALIBRATION_MEASURE_UMIN
//#define CALIBRATION_MEASURE_UMAX
//#define CALIBRATION_MEASURE_VMIN
//#define CALIBRATION_MEASURE_VMAX
//#define CALIBRATION_MEASURE_WMIN
//#define CALIBRATION_MEASURE_WMAX
// Probing at the exact top center only works if the center is flat. If
// probing on a screwhead or hollow washer, probe near the edges.
//#define CALIBRATION_MEASURE_AT_TOP_EDGES
// Define the pin to read during calibration
#ifndef CALIBRATION_PIN
//#define CALIBRATION_PIN -1 // Define here to override the default pin
#define CALIBRATION_PIN_INVERTING false // Set to true to invert the custom pin
//#define CALIBRATION_PIN_PULLDOWN
#define CALIBRATION_PIN_PULLUP
#endif
#endif
/
* Adaptive Step Smoothing increases the resolution of multi-axis moves, particularly at step frequencies
* below 1kHz (for AVR) or 10kHz (for ARM), where aliasing between axes in multi-axis moves causes audible
* vibration and surface artifacts. The algorithm adapts to provide the best possible step smoothing at the
* lowest stepping frequencies.
*/
//#define ADAPTIVE_STEP_SMOOTHING
/
* Custom Microstepping
* Override as-needed for your setup. Up to 3 MS pins are supported.
*/
//#define MICROSTEP1 LOW,LOW,LOW
//#define MICROSTEP2 HIGH,LOW,LOW
//#define MICROSTEP4 LOW,HIGH,LOW
//#define MICROSTEP8 HIGH,HIGH,LOW
//#define MICROSTEP16 LOW,LOW,HIGH
//#define MICROSTEP32 HIGH,LOW,HIGH
// Microstep settings (Requires a board with pins named X_MS1, X_MS2, etc.)
#define MICROSTEP_MODES { 16, 16, 16, 16, 16, 16 } // [1,2,4,8,16]
/
* @section stepper motor current
*
* Some boards have a means of setting the stepper motor current via firmware.
*
* The power on motor currents are set by:
* PWM_MOTOR_CURRENT - used by MINIRAMBO & ULTIMAIN_2
* known compatible chips: A4982
* DIGIPOT_MOTOR_CURRENT - used by BQ_ZUM_MEGA_3D, RAMBO & SCOOVO_X9H
* known compatible chips: AD5206
* DAC_MOTOR_CURRENT_DEFAULT - used by PRINTRBOARD_REVF & RIGIDBOARD_V2
* known compatible chips: MCP4728
* DIGIPOT_I2C_MOTOR_CURRENTS - used by 5DPRINT, AZTEEG_X3_PRO, AZTEEG_X5_MINI_WIFI, MIGHTYBOARD_REVE
* known compatible chips: MCP4451, MCP4018
*
* Motor currents can also be set by M907 - M910 and by the LCD.
* M907 - applies to all.
* M908 - BQ_ZUM_MEGA_3D, RAMBO, PRINTRBOARD_REVF, RIGIDBOARD_V2 & SCOOVO_X9H
* M909, M910 & LCD - only PRINTRBOARD_REVF & RIGIDBOARD_V2
*/
//#define PWM_MOTOR_CURRENT { 1300, 1300, 1250 } // Values in milliamps
//#define DIGIPOT_MOTOR_CURRENT { 135,135,135,135,135 } // Values 0-255 (RAMBO 135 = ~0.75A, 185 = ~1A)
//#define DAC_MOTOR_CURRENT_DEFAULT { 70, 80, 90, 80 } // Default drive percent - X, Y, Z, E axis
/
* I2C-based DIGIPOTs (e.g., Azteeg X3 Pro)
*/
//#define DIGIPOT_MCP4018 // Requires https://github.com/felias-fogg/SlowSoftI2CMaster
//#define DIGIPOT_MCP4451
#if EITHER(DIGIPOT_MCP4018, DIGIPOT_MCP4451)
#define DIGIPOT_I2C_NUM_CHANNELS 8 // 5DPRINT:4 AZTEEG_X3_PRO:8 MKS_SBASE:5 MIGHTYBOARD_REVE:5
// Actual motor currents in Amps. The number of entries must match DIGIPOT_I2C_NUM_CHANNELS.
// These correspond to the physical drivers, so be mindful if the order is changed.
#define DIGIPOT_I2C_MOTOR_CURRENTS { 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0, 1.0 } // AZTEEG_X3_PRO
//#define DIGIPOT_USE_RAW_VALUES // Use DIGIPOT_MOTOR_CURRENT raw wiper values (instead of A4988 motor currents)
Артем, [16.09.2024 16:46]
/
* Common slave addresses:
*
* A (A shifted) B (B shifted) IC
* Smoothie 0x2C (0x58) 0x2D (0x5A) MCP4451
* AZTEEG_X3_PRO 0x2C (0x58) 0x2E (0x5C) MCP4451
* AZTEEG_X5_MINI 0x2C (0x58) 0x2E (0x5C) MCP4451
* AZTEEG_X5_MINI_WIFI 0x58 0x5C MCP4451
* MIGHTYBOARD_REVE 0x2F (0x5E) MCP4018
*/
//#define DIGIPOT_I2C_ADDRESS_A 0x2C // Unshifted slave address for first DIGIPOT
//#define DIGIPOT_I2C_ADDRESS_B 0x2D // Unshifted slave address for second DIGIPOT
#endif
//===========================================================================
//=============================Additional Features===========================
//===========================================================================
// @section lcd
#if HAS_MANUAL_MOVE_MENU
#define MANUAL_FEEDRATE { 50*60, 50*60, 4*60, 2*60 } // (mm/min) Feedrates for manual moves along X, Y, Z, E from panel
#define FINE_MANUAL_MOVE 0.025 // (mm) Smallest manual move (' and list long filenames with 'M20 L'
//#define LONG_FILENAME_WRITE_SUPPORT // Create / delete files with long filenames via M28, M30, and Binary Transfer Protocol
//#define M20_TIMESTAMP_SUPPORT // Include timestamps by adding the 'T' flag to M20 commands
//#define SCROLL_LONG_FILENAMES // Scroll long filenames in the SD card menu
//#define SD_ABORT_NO_COOLDOWN // Leave the heaters on after Stop Print (not recommended!)
/
* Abort SD printing when any endstop is triggered.
* This feature is enabled with 'M540 S1' or from the LCD menu.










Комментарии и вопросы
сначала лайкнул а потом подума...
Так-то оно конечно, не настоль...
Да, PETg разный (в т.ч. углена...
Плата разветвивтель на несколь...
Принтер Creality K2 с хранилищ...
Например на нижнем или верхнем...
Ну например послал на печать и...